Using weak partitioning chromatography with AEX as the only polishing step has also been proposed as a possible efficient platform (5, 6). Compared to more typical flow-through chromatography, here the conductivity and pH are chosen such that the binding of both the product and impurities are enhanced, attaining an antibody partition coefficient (Kp) between 0.1-20, and preferably between 1 and 3. While both the antibody and impurities bind to the anion exchange resin, the impurities are much more tightly bound than in flow-through mode resulting in significantly higher impurity clearance. Load capacity (>1500 g/L) may be achievable with > 95% product recovery and robust process performance.
Monoclonal antibodies expressed in yeast
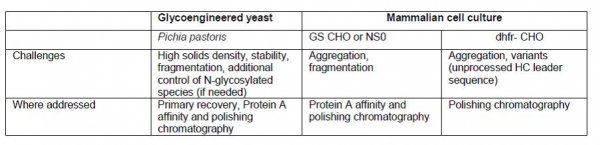
While mammalian cells (e.g., such as Chinese hamster ovary [CHO]), have been the primary expression system for mAb products; other expression systems such as yeast have also been proposed. Table I summarizes some of the process development challenges with mAb quality from the various expression systems and the tools and unit operations options for addressing these challenges.
While mammalian cells (e.g., such as Chinese hamster ovary [CHO]), have been the primary expression system for mAb products; other expression systems such as yeast have also been proposed. Table I summarizes some of the process development challenges with mAb quality from the various expression systems and the tools and unit operations options for addressing these challenges.
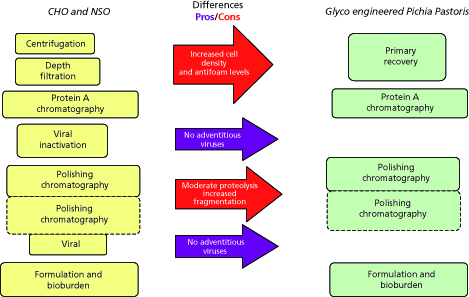
Further, Figure 4 shows the application of a modular approach for selecting the right modules in the case of purifying mAbs expressed in glycoengineered Pichia pastoris. As shown below, while the primary recovery module is kept as part of the flow scheme, it requires optimization to work with increased solids density, media components, and other metabolites. On the other hand, because of the absence of adventitious viruses in glycoengineered Pichia pastoris, viral inactivation and viral filtration steps, which are part of mammalian cell culture-derived mAb processes, are no longer needed. Primary recovery and initial capture conditions are also optimized to minimize any potential proteolysis from the Pichia pastoris host.