Use of multimodal chromatography
Recently, mixed-mode, ion-exchange ligands with enhanced binding strength for aggregates through the addition of hydrophobic functionality have been brought to market. These resins combine different types of interactions such as ionic interaction, hydrogen bonding, and hydrophobic interaction. This can result in a different selectivity than what is offered by traditional ion-exchange or hydrophobic interaction chromatography, thus offering a larger range of ionic strength and pH under which significant separation can occur (6,7).
Mixed-mode resins based on hydroxyapatite, made from calcium phosphate, have both positive and negative charges and interact with proteins through a combination of electrostatic interactions and coordination complex formation. Traditionally, hydroxyapatite has been used for separation of protein therapeutics from host and media proteins, aggregates, DNA, and Protein A, all of which tend to bind more tightly.
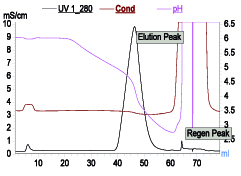
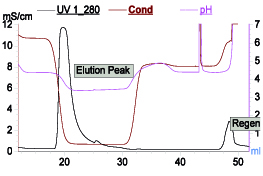
Mixed-mode resins based on ion exchange along with multimodal interactions can offer single-step operation as an alternative to two-step process of ion exchange and HIC. One such example is Capto Adhere (Cytiva, Uppsala, Sweden). It can be operated as anion exchanger as well as hydrophobic mode by applying suitable process condition. In another example MEPHyperCel (Pall Corp., East Hills, NY) resin operates via mixed-mode interactions governed by hydrophobic charge-induction chromatography (HCIC). HCIC is based on pH-dependent behavior of ionizable dual-mode ligand. Binding of protein is based on mild hydrophobic interaction and conducted at near-neutral pH condition where the pyridine group of the ligand is uncharged. Protein desorption is prompted by electrostatic charge repulsion by decreasing the pH. This desorption can be further enhanced by decreasing hydrophobicity. As in HCIC, protein binding can take place at relatively less salt concentration, thus offering an alternative to HIC where high salt requirement for binding is a cumbersome operation. One such profile is shown in Figure 5. It can be operated entirely based on pH or salt with slight change in pH. This resin can also be used as a step for capture step.
These resins offer a different selectivity than the traditional ion exchange and hydrophobic interaction chromatography and are likely to make inroads into many process platforms over time as users create new applications around them.